Introduction to Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy, a molecular spectroscopy which is observed as inelastically scattered light, allows for the interrogation and identification of vibrational (phonon) states of molecules. As a result, Raman spectroscopy provides an invaluable analytical tool for molecular fingerprinting as well as monitoring changes in molecular bond structure (e.g. product formation; state changes and stresses & strains; crystalline form and crystallinity).
 In comparison to other vibrational spectroscopy methods, such as FTIR and NIR, Raman has several major advantages. These advantages stem from the fact that the Raman effect manifests itself in the light scattered off of a sample as opposed to the light absorbed by a sample. As a result, Raman spectroscopy requires little to no sample preparation and is insensitive to aqueous absorption bands. This property of Raman facilitates the measurement of solids, liquids, and gases not only directly, but also through transparent containers such as glass, quartz, and plastic.
In comparison to other vibrational spectroscopy methods, such as FTIR and NIR, Raman has several major advantages. These advantages stem from the fact that the Raman effect manifests itself in the light scattered off of a sample as opposed to the light absorbed by a sample. As a result, Raman spectroscopy requires little to no sample preparation and is insensitive to aqueous absorption bands. This property of Raman facilitates the measurement of solids, liquids, and gases not only directly, but also through transparent containers such as glass, quartz, and plastic.
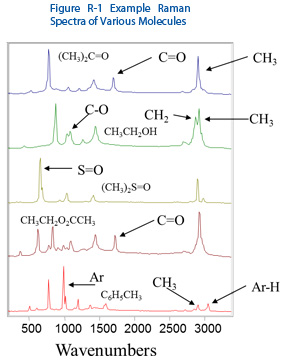
Raman spectroscopy is highly selective, as is the complementary method of FTIR , which allows it to identify and differentiate molecules and chemical species that are very similar, and measure small changes in samples. Figure R-1 shows an example of five molecules – Acetone, Ethanol, Dimethyl Sulfoxide, Ethyl Acetate, and Toluene, with peaks from specific functional groups marked. Although these organic solvents have similar molecular structure, their Raman spectra are clearly differentiable, even to the untrained eye. Using Raman spectral libraries, it is easy to see how easily Raman spectra can be used for material identification and verification.
Videos:
Educational Video Series: Episode 6 – Raman Spectroscopy
Educational Video Series: Season 3 Episode 3- The Raman Effect
Application Videos:
https://bwtek.com/videos-applications/
Read about some applications of Raman:
https://bwtek.com/category/laboratory-raman-app-notes
The advantages of a Compact TE-Cooled Fiber Optic Spectrometer for Raman and Fluorescence
Products:
Portable Raman
Handheld Raman







