
DIY Extended Range Raman (Concatenation)
Our DIY Extended Range Raman system combines wide range Raman spectral coverage and excellent spectral resolution by utilizing an 860 nm/1064 nm laser combination to overcome the typical range/resolution trade-off with traditional dispersive 1064 nm Raman systems.
Concatenation Raman System
Our 860/1064 DIY Extended Range Raman system is ideal for many of the more challenging applications for Raman analysis without sacrificing data quality, spectral coverage, or resolution.
The 860/1064 DIY Extended Range Raman system includes:
1. Research-grade Sol HT 1.4 spectrometer, providing extended Raman coverage from 200 to 4600 cm-1, while providing a resolution of 10 cm-1.
2. Configurable Raman Probe designed for dual-wavelength operation in a single probe body.
3. Turn-Key dual-wavelength laser system.
Applications for Raman Concatenation
When samples have strong fluorescence, Raman concatenation allows for shifting the fingerprint excitation laser to longer wavelengths, even 1064 nm, and still allows for measuring the Raman stretch region by using an 860 nm laser, enabling the measurement of aliphatic and aromatic C-H stretch differences, compounds with N-H stretches, and even the elusive water O-H stretch which extends out to beyond 3600 nm.
Food and Beverage
The USDA requires jerky to maintain a moisture-to-protein ratio (MPR) below 0.75:1 and a water activity (aW) under 0.60 to prevent microbial growth and spoilage.
Concatenated Raman spectroscopy is well-suited for this analysis, as its dual-laser system captures protein peaks in the fingerprint region and O–H/C–H stretch peaks in the high Raman shift region, enabling fast, non-destructive monitoring of both moisture and protein content.
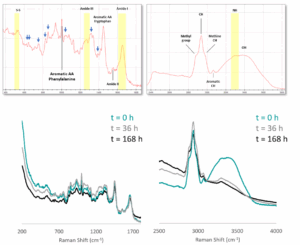
Polymers
During curing, amine and epoxy groups form polymer networks, causing Raman signals to shift as bonds are consumed and new structures form.
These changes appear in both the fingerprint and stretch regions but are more pronounced in the stretch region. The N–H peak can also be used for Amine Value Prediction, making Concatenated Raman a powerful tool for monitoring and optimizing polymerization.
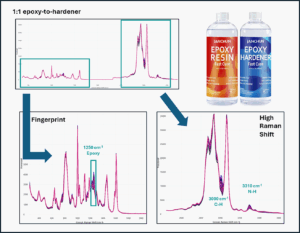
Plant Health
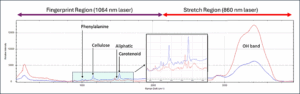
Plant-based monitoring, where the Fingerprint Region provides data on the structural compounds and carotenoids, and the Stretch Region allows simultaneous monitoring of water content and plant stress. Below is an example of a typical spectrum of a plant sample.
Chemical Production
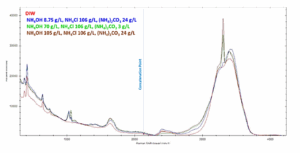
Soda ash (Na₂CO₃), essential for glass, detergents, and water softening, is primarily produced through the Solvay process, where monitoring ammonia-based chemistries is critical.
With extended spectral coverage up to 4600 cm⁻¹, Concatenated Raman spectroscopy can detect N–H bonds (~3300 cm⁻¹), providing a powerful tool for real-time process control and improved efficiency in soda ash production.
Raman Concatenation Brochure
Raman Concatenation is an exciting new technique, and it involves sequentially collecting Raman spectra from two NIR lasers with one Raman spectrometer and one Raman probe. It enables fluorescence free spectra of the fingerprint and stretching region with increased sensitivity and discrimination.
Build Your Own DIY Raman System
Reach out to connect with an expert and start building an optimized system today!
Contact Us